3D Printer
What is 3D printer?
A 3D printer is a device that creates a three dimensional model of an object through the process of additive manufacturing. The printer deposits material layer by layer, untill the desired object is completed. Using 3D
modeling software,such as AutoCAD or Blender a designer can create a printable model. 3D printers are primarily used for prototyping. but can also be used for arts and crafts. Like standard printers, the quality of the printer can determine the level of precision that the printer can achieve. Industrial,higher quality versions that produce larger or more detailed objects are called rapid prototyping machines.
 |
| 3D printer |
Types of 3D printer and their functions
This article is focused at the following 3D printing technologies or some may call them types of 3D printers:
- Stereolothography(SLA);
- Digital Light Processing(DLP);
- Fused Deposition Modeling(FDM);
- Selective Laser Sintering(SLS);
- Selective Laser Melting(SLM);
- Electyonic Beam Melting(EBM);
- Laminated Object Manufacturing(LOM).
Stereolithography(SLA)
 |
| Stereolithography(SLA) |
Stereolithography (SLA) is an additive manufacturing - commonly referred to as 3D printing - technology that converts liquid materials into solid parts, layer by layer, by selectively curing them using a light source in a process called photopolymerization. SLA is widely used to create models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts for a range of industries from engineering and product design to manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry, model making, and education
Uses:
- Medical modelling: Stereolithographic models have been used in medicine since the 1990s, for creating accurate 3D models of various anatomical regions of a patient, based on datasets from computer scans.
- Prototyping: Stereolithography is often used for prototyping parts. For a relatively low price, Stereolithography can produce accurate prototypes, even of irregular shapes. Businesses can use those prototypes to assess the design of their product or as publicity for the final product.
Digital Light Processing(DLP)
 |
| Digital Light Processing(DLP) |
DLP Digital Light Processing rapid prototyping services is a form of stereolithography that is used in rapid prototyping services. The main difference between DLP and SLA rapid prototyping is the use of a projector light rather than a laser to cure photo-sensitive polymer resin. A DLP 3D printer projects the image of the object’s cross section onto the surface of the resin. The exposed resin hardens while the machine’s build platform descends, setting the stage for a new layer of fresh resin to be coated to the object and cured by light. Once a complete object is formed, additional post processing may be required such as removal of support material, chemical bath, and UV curing (upon request). Digital Light Processing rapid prototyping services will produce parts with resolutions under 30 microns; the equivalent to other stereolithography machines. Ultimately, production time does depend on the size of the model. Compared to FDM, DLP 3D printing provides higher resolution and smoother surfaces.DLP prototyping equipment utilizes a standard office digital projector as its main light source. These projectors can be purchased at various retail stores and are included in many do it yourself DLP kits.
Uses:
- Rapid prototyping
- Fit and function models
- Molds for tooling and metal casting
- Hearing aids and medical implants
- Dental restorations
- Jewelry casting
- Automotive components
- Aerospace components
Fused Deposition Modeling(FDM)
 |
| Fused Deposition Modeling(FDM) |
Fused Deposition Modeling rapid prototyping is a 3D printing process used by today’s desktop units with industrial units available as well. This process uses thermoplastic material which is first melted then extruded from a moving nozzle. FDM prototyping printers use a spool of wire-
shaped filament that often consists of ABS or PLA plastic, although additional materials such as Nylon, PVA, TPE, Soft PLA, Laybrick, Laywood, and HDPE can be used.In FDM prototyping services, a gear system pushes filament toward the nozzle. As it approaches the heating assembly, it’s melted beyond its glass transition temperature and deposited onto the build surface. The nozzle itself moves about the X and Y axes, driven by a predetermined numerically controlled tool-path. As each cross-sectional layer is extruded, the build platform (Z axis) moves downward setting up position for the next successive layer of melted material. The process is repeated until these many layers form a physical 3D print.
Selective Laser Sintering(SLS)
 |
| Selective Laser Sintering(SLS) |
SLS Selective Laser Sintering 3d printing services involve the use of a laser to sinter powdered metal, plastic, glass, or ceramics into a 3D object. A roller spreads an even coat of powder over the build surface. A high powered laser traces a cross-sectional shape of the object into the powdered material. The sintered particles fused together forming the first solid layer of the object. The powder coated build surface moves downward one layer at a time after each trace. The process is repeated layer by layer until a complete 3D object is formed. SLS rapid prototyping sinters material, but does not actually melt it.Selective laser sintering prototyping services do not require support material for complex parts. Since the part is supported by loose unsintered powder, various complex shapes and geometries can be achieved. Typically, selective laser sintering 3D printing services will use dual mixture powders. This consists of the actual powder (metal, plastic, etc.) particulate combined with a material to provide a catalyst for sintering. Post processing a SLS prototyped parts usually consists of air blasting to remove excess particles.
Selective Laser Melting(SLM)
 |
| Selective Laser Melting(SLM) |
SLM (Selective Laser Melting) is in an additive manufacturing method specially developped for 3D Printing metal alloys. It creates parts additively by fusing metal powder particles together in a full melting process. Like in the SLS process, your metal part will be created layer by layer, according to your 3D model. Unlike DMLS, SLM fully melts the powder, and therefore it needs to reach a higher temperature than this other metal 3D printing technique. The build chamber is filled with an inert gas (either argon or nitrogen at oxygen levels below 500 parts per million) in order to create the perfect conditions for melting.The full melting process allows the metal to form a homogeneous block with good resistance. It fits perfectly for pure metals like titanium or aluminum.Because we need the higher temperature to fully melt the material, the cooling time will be longer than for DMLS.The steps of the SLM process are the same as other laser-based additive technologies: first of all a roller will apply a layer of metal powder, then the laser will sinter the powder according to the 3D file, and the build platform will get down before
applying a new layer of powder... The process will be repeated until the desired part is created. Once it's finished, the metal part needs to cool down before being extracted.
Electyonic Beam Melting(EBM)
 |
| Electyonic Beam Melting(EBM) |
Electron beam melting or EBM is a type of additive manufacturing that is classified as a power bed fusion technique that was originally patented and developed by Arcam AB. EBM uses an electron beam as the power source instead of a laser to 3D print metal. An electron beam melts metal powder layer by layer in a high vacuum and can achieve full melting of the metal powder. This method can produce fully dense metal parts and can retain the characteristics of the material. The Electron Beam Melting process can produce metal parts with 100% density and its material properties are much better than cast metals. The EBM process takes place in a vacuum which makes this process perfect for manufacturing reactive materials with a high affinity for oxygen. This process also operates at higher temperatures (up to 1000°C).
Laminated Object Manufacturing(LOM)
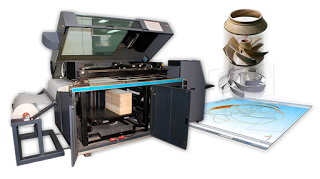 |
| Laminated Object Manufacturing(LOM) |
OurLOM Laminated Object Manufacturing 3d printing services bind together thin sheets of paper, plastic, or metal using a specialized adhesive. At the same time, the LOM 3D printer will use a blade or laser to cut a cross sectional outline of that object. A new sheet of material is laid down and the process is repeated until an entire 3D object is created. Excess material surrounding the object is removed at the end of the print.As the sheet is placed down, an adhesive is applied to specific areas of the design. A heated roller goes over the sheet and applies pressure followed by a laser or knife that traces a 2D cross sectional area of the object into the material. The cut paper is separated as the build platform descends and loads a new sheet of material to prepare for the next layer.








No comments